CSS margin vs Padding, When it comes to web design and layout, two essential CSS properties play a crucial role in controlling the spacing around elements: margin and padding. While they may appear similar at first glance, understanding the differences between them is key to crafting visually appealing and well-structured web pages. In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of CSS margin and padding, exploring their definitions, purposes, usage scenarios, and best practices. So let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of these fundamental CSS properties.
Defining Margin and Padding
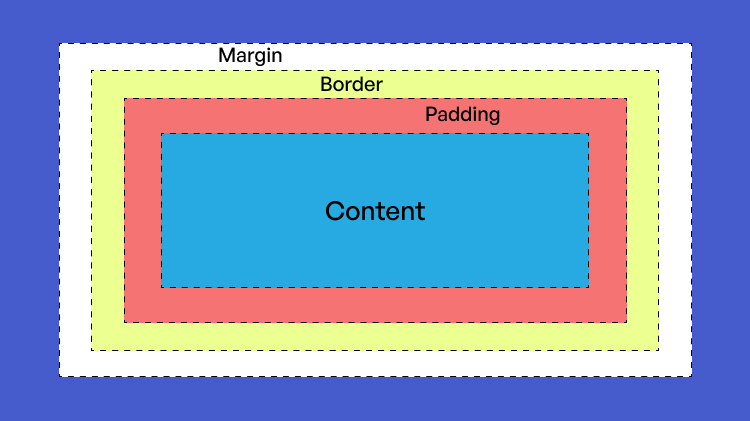
In CSS, margin and padding are box-model properties that control the space around and within an element, respectively.
1. Margin: Margin refers to the space outside an element’s borders. It creates a transparent area that separates an element from its neighboring elements. It controls the spacing between elements and helps create visual separation. Negative margins can be used to overlap elements.
2. Padding: Padding refers to the space within an element, between its content and borders. It provides internal space and helps maintain a distance between the element’s content and its borders. Padding affects the size and layout of an element without affecting neighboring elements.
Understanding the Differences
While both margin and padding control spacing, there are significant differences between the two:
1. Relationship to Borders: Margin is the space outside an element’s borders, whereas padding is the space within an element, between its content and borders. Margins are considered part of the external area of an element, while padding is part of its internal area.
2. Impact on Element Sizing: Margin affects the overall size and layout of an element, as it adds to the total space occupied by the element, potentially increasing its dimensions. Padding, on the other hand, does not affect the element’s dimensions, as it only adds space within the element.
3. Collapsing Margins: Margins have a unique behavior called margin collapsing, where adjacent margins collapse into a single margin. This occurs when the top and bottom margins of two elements are touching or overlapping. Padding does not exhibit this behavior.
Usage Scenarios and Best Practices
Both margin and padding offer flexibility in designing web layouts. Understanding their appropriate usage is crucial for effective web design. Here are some common scenarios and best practices for utilizing margin and padding:
1. Margin Usage:
– Creating Spacing Between Elements: Use margin to establish space between elements, providing visual separation and preventing them from appearing cramped.
– Margin Auto for Centering: Use `margin: auto` on an element with a defined width to horizontally center it within its parent container.
– Negative Margins for Overlapping Effects: In some cases, negative margins can be used to create overlapping effects, such as image overlays or floating elements.
2. Padding Usage:
– Controlling Element Content Placement: Use padding to provide internal space within an element, ensuring proper placement and spacing of the content.
– Enhancing Readability: Apply padding to text elements, such as paragraphs or headings, to enhance readability by adding space around the text.
– Building Responsive Designs: Utilize padding to create responsive designs that adjust spacing and maintain a consistent appearance across different screen sizes.
Best Practices:
– Maintain Consistency: Maintain consistent margin and padding values across elements of the same type to ensure a harmonious and balanced layout.
– Use Responsive Units: Consider using relative units like percentages or `em` instead of fixed pixels for margin and padding values, allowing for better responsiveness.
– Be Mindful of Collapsing Margins: Understand the behavior of margin collapsing and account for it when designing layouts to achieve the desired spacing between elements.
Conclusion
CSS margin and padding are fundamental properties that control the spacing within and around elements. While margin determines the space outside an element’s borders, padding controls the space within. By understanding their differences and best practices, web designers can create visually appealing and well-structured web pages.